How to operate a drone safely and effectively is a skill that opens up a world of exciting possibilities, from breathtaking aerial photography to innovative surveying techniques. This guide provides a structured approach to learning, covering everything from understanding basic components and pre-flight checks to mastering advanced maneuvers and adhering to legal regulations. Whether you’re a complete beginner or looking to refine your existing skills, this comprehensive resource will equip you with the knowledge and confidence to take to the skies responsibly.
We’ll explore the intricacies of drone mechanics, navigating the nuances of controls and flight modes. You’ll discover how to capture stunning aerial imagery, troubleshoot common problems, and understand the legal framework governing drone operation. By the end, you’ll be prepared to embark on your own aerial adventures with skill and confidence.
Drone Components and Terminology
Understanding the individual parts of your drone and the terminology used in drone operation is crucial for safe and effective flight. This section details the key components and defines common terms.
Drone Components and Their Functions
A drone’s functionality relies on the coordinated operation of several key components. Each plays a vital role in enabling flight and capturing aerial footage.
- Propellers: These rotating blades generate the thrust necessary for lift and maneuverability. Different propeller designs offer varying levels of thrust and efficiency.
- Motors: Electric motors power the propellers, converting electrical energy into mechanical rotation. The speed and direction of motor rotation are controlled by the flight controller.
- Flight Controller: The brain of the drone, this sophisticated computer receives input from various sensors and controls the motors to maintain stability and execute flight commands. It processes data from the GPS, IMU (Inertial Measurement Unit), and other sensors.
- Battery: Provides the electrical power for all drone components. The flight time is directly related to the battery’s capacity and the drone’s power consumption.
- GPS (Global Positioning System): Enables precise location tracking, allowing for features like GPS-assisted flight, Return-to-Home (RTH), and waypoint navigation. A strong GPS signal is essential for stable and accurate flight.
- Camera: Captures high-resolution photos and videos. Many drones offer adjustable camera settings such as ISO, shutter speed, and aperture, providing control over image quality.
Glossary of Common Drone Terminology
Familiarizing yourself with common drone terms is essential for understanding flight instructions and troubleshooting issues.
- Yaw: Rotation of the drone around its vertical axis (spinning left or right).
- Pitch: Movement of the drone’s nose up or down.
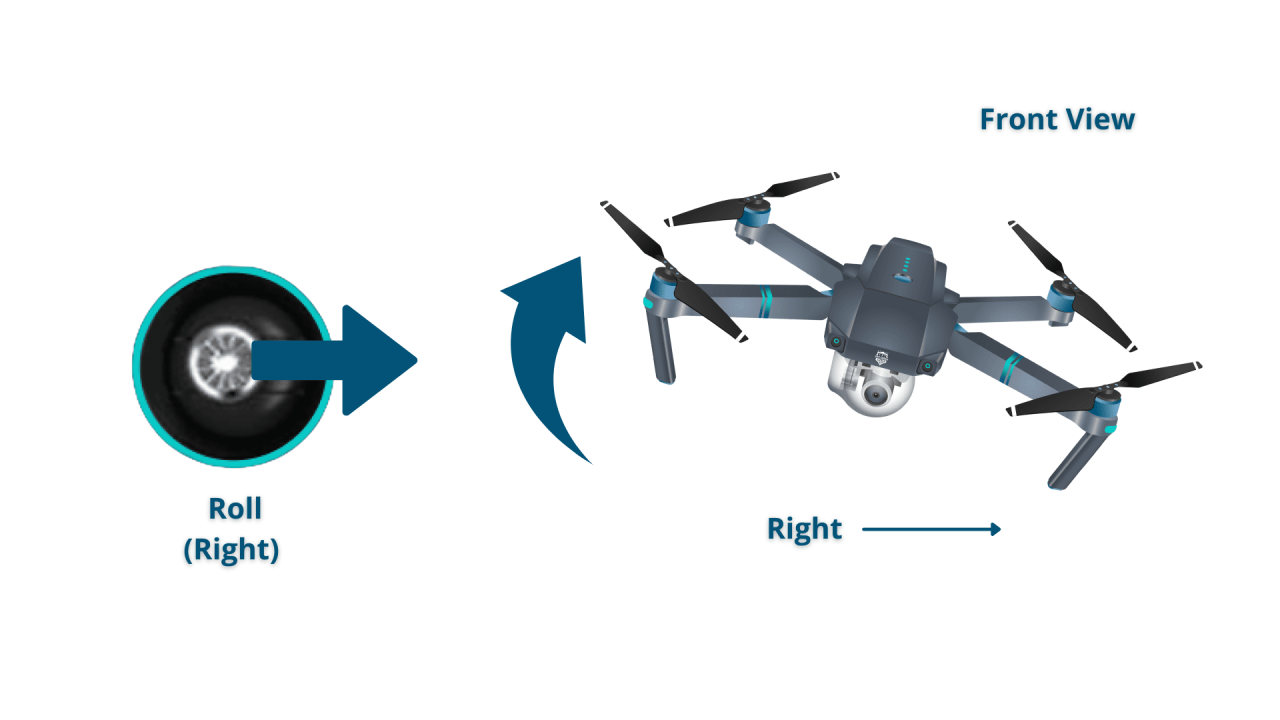
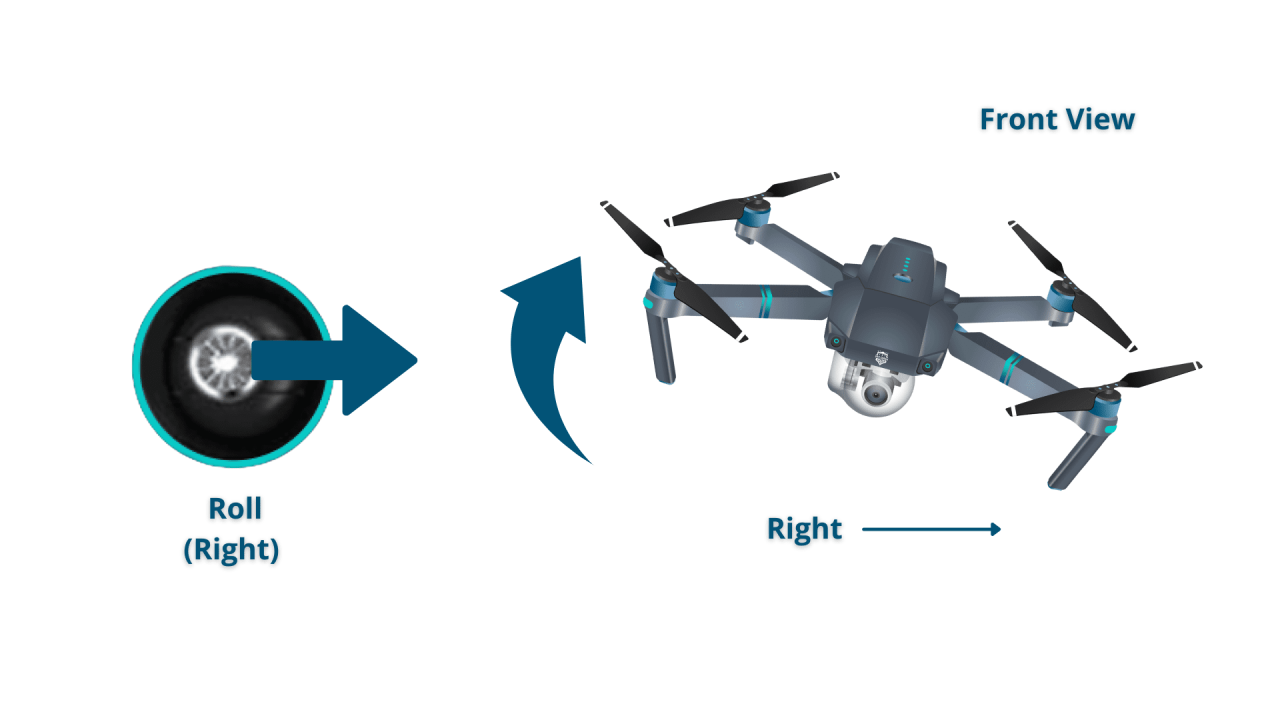
- Roll: Tilting the drone left or right.
- Altitude Hold: A flight mode that maintains a constant altitude, simplifying hovering and preventing unintentional ascents or descents.
- Waypoint: A pre-programmed location in a flight plan that the drone will automatically navigate to.
Comparison of Drone Battery Types
Different battery types offer various advantages and disadvantages. Understanding these differences is crucial for choosing the right battery for your drone and flight needs.
| Battery Type | Pros | Cons | Typical Applications |
|---|---|---|---|
| LiPo (Lithium Polymer) | High power density, lightweight | Requires careful handling, limited cycle life, potential for fire if mishandled | Most common type for hobby and professional drones |
| LiHV (Lithium Polymer High Voltage) | Higher voltage than LiPo, longer flight times | More expensive than LiPo, requires specialized chargers | Used in high-performance drones requiring extended flight times |
Pre-Flight Checklist and Safety Procedures

A thorough pre-flight checklist and adherence to safety guidelines are paramount for safe drone operation. Neglecting these steps can lead to accidents and damage.
Pre-Flight Checklist
Before each flight, perform a comprehensive inspection to ensure the drone is in optimal condition. This checklist helps to avoid potential issues during flight.
- Check battery charge level and ensure it is fully charged.
- Inspect propellers for damage or cracks.
- Verify GPS signal strength and accuracy.
- Check all connections and ensure everything is securely fastened.
- Review the planned flight path and ensure it is safe and legal.
- Calibrate the drone’s sensors if necessary.
Drone Safety Guidelines
Safe drone operation requires careful consideration of airspace regulations and potential hazards. Responsible flying minimizes risks and ensures the safety of others.
- Always fly within legal limits and respect airspace restrictions.
- Avoid flying near airports, power lines, and other obstacles.
- Maintain visual line of sight with the drone at all times.
- Never fly over crowds or people.
- Be aware of weather conditions and avoid flying in adverse weather.
Pre-Flight Inspection Flowchart
A visual representation of the pre-flight inspection process aids in ensuring no steps are missed.
The flowchart would visually depict the steps Artikeld in the pre-flight checklist above, using boxes and arrows to show the sequence of checks, with decision points (e.g., “Battery OK?”) leading to different paths.
Basic Drone Controls and Maneuvers
Understanding the basic controls and maneuvers is fundamental to operating a drone safely and effectively. This section covers the essentials of drone piloting.
Drone Remote Control Functions
Most drone remotes utilize two control sticks and several buttons to manage various aspects of the drone’s operation.
- Left Stick: Typically controls altitude and yaw.
- Right Stick: Usually controls pitch and roll.
- Buttons: Various buttons on the remote control typically activate functions like taking off, landing, returning home, and switching flight modes.
Basic Flight Maneuvers
Mastering these basic maneuvers is crucial for confident and controlled drone operation.
- Taking Off: Gently increase throttle (typically the left stick upward) to lift the drone vertically.
- Landing: Slowly lower the throttle (left stick downward) to bring the drone gently to the ground.
- Hovering: Maintain a steady throttle position to keep the drone suspended in the air.
- Directional Movements: Use the right stick to control pitch (forward and backward) and roll (left and right).
Executing a Simple Flight Pattern
Practicing a simple flight pattern helps build confidence and coordination with the drone’s controls.
- Take off and hover.
- Move forward in a straight line for a set distance.
- Turn 90 degrees to the right (yaw).
- Move forward again.
- Repeat steps 2 and 3 until a square pattern is completed.
- Return to the starting point and land.
Advanced Drone Flight Techniques

Once comfortable with basic maneuvers, you can explore more advanced flight techniques. These maneuvers require practice and precision.
Advanced Maneuvers
Many drones, particularly those designed for acrobatic flight, offer advanced maneuvers. These often require specific flight modes and precise control.
- Flips: Rapid rotations of the drone around its axes (e.g., forward, backward, left, right).
- Rolls: Rotations around the drone’s longitudinal axis.
- Other Acrobatic Movements: These can include barrel rolls, helixes, and other complex aerial maneuvers, varying by drone model and capabilities.
Flight Modes
Different flight modes offer varying levels of control and stability. Understanding their differences is crucial for adapting to different situations.
Understanding drone operation involves several key steps, from pre-flight checks to mastering the controls. Successfully navigating these steps requires a good understanding of the technology and regulations. For a comprehensive guide covering all aspects, from basic controls to advanced maneuvers, check out this excellent resource on how to operate a drone. Safe and responsible drone operation is paramount, ensuring both your safety and the safety of others.
- GPS Mode: Relies on GPS for position and altitude holding, providing stability and ease of control.
- Attitude Mode: Maintains the drone’s orientation but doesn’t use GPS for position holding, allowing for more agile maneuvers but requiring more precise control.
- Manual Mode: Offers full manual control, but requires significant piloting skill and is generally less stable.
Setting Waypoints and Creating Autonomous Flight Plans
Many drones allow for pre-programming flight paths using waypoints. This allows for automated flights, freeing up the pilot’s attention for camera operation or other tasks.
The process typically involves using drone-specific software or mobile applications to define a series of waypoints on a map. The drone will then automatically navigate between these points, following the pre-determined flight path.
Drone Camera Operation and Photography
Capturing stunning aerial photos and videos requires understanding camera settings and composition techniques. This section explores these aspects.
Adjusting Camera Settings
Optimal image quality relies on correctly adjusting camera settings based on lighting conditions and desired effects.
- ISO: Controls the sensitivity to light. Lower ISO values are better in bright light, while higher values are needed in low light, but can increase noise.
- Shutter Speed: Determines how long the camera’s sensor is exposed to light. Faster shutter speeds freeze motion, while slower speeds can create motion blur.
- Aperture: Controls the size of the lens opening, affecting depth of field. A wider aperture (smaller f-number) creates a shallow depth of field, blurring the background, while a narrower aperture (larger f-number) increases depth of field.
Capturing High-Quality Aerial Photos and Videos
Several factors contribute to high-quality aerial imagery.
- Proper Lighting: Avoid harsh midday sun; “golden hour” (sunrise and sunset) lighting is often ideal.
- Stable Shots: Use appropriate flight modes to minimize vibrations and camera shake.
- Composition: Apply the rules of composition (discussed below) to create visually appealing images.
Composition Techniques for Drone Photography
Effective composition enhances the visual appeal of your aerial images.
- Rule of Thirds: Place key elements along imaginary lines that divide the frame into thirds, both horizontally and vertically.
- Leading Lines: Use natural lines (roads, rivers) to draw the viewer’s eye through the image.
- Symmetry and Patterns: Capture symmetrical scenes or repeating patterns for visually striking results.
- Perspective: Use altitude and angle to create unique and compelling perspectives.
Drone Maintenance and Troubleshooting
Regular maintenance and prompt troubleshooting are vital for keeping your drone in optimal condition and extending its lifespan. This section provides guidance on these aspects.
Common Drone Problems and Solutions, How to operate a drone
Identifying and addressing common problems promptly can prevent more serious issues.
- Low Battery: Charge the battery fully. Consider using higher capacity batteries for longer flight times.
- GPS Signal Loss: Fly in an open area with a clear view of the sky. Ensure the GPS module is functioning correctly.
- Motor Failure: Inspect motors for damage. Replace any faulty motors.
Cleaning and Maintaining Drone Components
Regular cleaning helps prevent the accumulation of dust and debris that can affect performance.
- Use a soft brush or compressed air to remove dust from the drone’s body and propellers.
- Clean the camera lens with a microfiber cloth.
- Inspect all connections and tighten any loose screws.
- Store the drone in a clean, dry place.
Sensor Calibration
Regular calibration of the drone’s sensors ensures accurate flight performance and stability.
The specific calibration procedure varies depending on the drone model. Consult your drone’s manual for detailed instructions. Typically, this involves performing a series of maneuvers to allow the drone to recalibrate its internal sensors.
Legal and Regulatory Compliance: How To Operate A Drone
Operating a drone responsibly involves understanding and adhering to all applicable laws and regulations. This section Artikels key legal considerations.
Legal Requirements for Drone Operation
Drone regulations vary by region. It’s crucial to research and comply with the specific rules in your area.
This typically involves registering your drone, obtaining necessary licenses or permits, and adhering to airspace restrictions. Failure to comply can result in fines or legal action.
Successfully operating a drone involves understanding its controls and adhering to safety regulations. Learning the basics is crucial before taking flight, and a great resource for this is the comprehensive guide on how to operate a drone , which covers everything from pre-flight checks to advanced maneuvers. Mastering these skills ensures safe and responsible drone operation.
Prohibited and Restricted Airspace
Certain areas are designated as no-fly zones for drones. These typically include airports, military bases, and other sensitive locations.
Before flying, use online resources or apps to check for airspace restrictions in your intended flight area. These resources provide up-to-date information on restricted areas.
Drone Regulations Across Different Countries
Drone regulations differ significantly across countries. Research the specific regulations of the country where you intend to fly.
Some countries have stricter regulations than others, including requirements for pilot licensing, operational permits, and limitations on drone types and capabilities.
Emergency Procedures
Knowing how to handle emergencies is crucial for safe drone operation. This section Artikels procedures for various emergency situations.
Handling Emergencies
Quick and decisive action is essential in emergency situations to minimize damage and ensure safety.
- Low Battery Warning: Immediately initiate a return-to-home procedure or find a safe place to land.
- Loss of Control: Attempt to regain control using available flight modes or emergency controls. If unsuccessful, prepare for an emergency landing.
- Unexpected Malfunctions: Attempt to troubleshoot the issue. If unable to resolve the problem, prioritize a safe emergency landing.
Safe Emergency Landing
In case of an emergency, prioritize a safe landing procedure.
- Assess the situation and identify a safe landing area.
- Slowly lower the throttle to descend.
- Maintain control of the drone’s orientation to avoid collisions.
- Once the drone touches down, turn off the power.
Emergency Checklist
A concise checklist helps ensure a calm and effective response during emergencies.
The checklist would list the steps to take in different emergency scenarios, providing a structured approach to handling unexpected situations.
Mastering the art of drone operation involves a blend of technical understanding, practical skills, and responsible decision-making. From understanding the fundamentals of flight mechanics to appreciating the legal and safety considerations, this guide has provided a framework for safe and proficient drone piloting. Remember, continuous practice and a commitment to safe operation are key to unlocking the full potential of this exciting technology.
Embrace the skies responsibly, and enjoy the unparalleled perspectives that await.
Popular Questions
What is the best type of drone for beginners?
Many user-friendly drones are ideal for beginners, often featuring GPS stabilization and autonomous flight modes. Research models known for their ease of use and robust safety features.
How often should I calibrate my drone?
Calibration frequency depends on usage. Regular calibration (every few flights or after a crash) ensures accurate sensor readings and optimal performance. Consult your drone’s manual for specific recommendations.
What should I do if I lose control of my drone?
If you lose control, prioritize safety. Attempt to regain control using failsafe mechanisms (if available). If unsuccessful, initiate an emergency landing procedure and contact local authorities if necessary.
How long does a drone battery typically last?
Drone battery life varies widely based on model, usage (flight style, camera use), and battery condition. Expect flight times ranging from 15-30 minutes, but always check the manufacturer’s specifications.